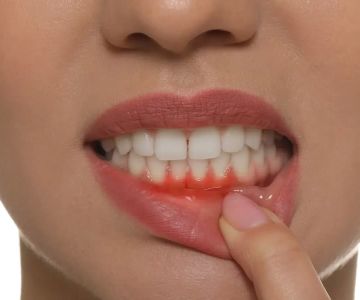
Understanding the Causes of Gum Bleeding or Pain
Gum bleeding or pain can stem from various sources. Poor oral hygiene is a common culprit, but it's not the only one. Smoking, gingivitis (early-stage gum disease), periodontitis (moderate to advanced gum disease), and other dental issues can cause gum problems. Beyond dental causes, conditions such as diabetes, hormone changes during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, vitamin deficiencies, blood-clotting disorders, and even stress can contribute to gum bleeding or pain.
Treatment Options for Gum Bleeding or Pain
The treatment for gum bleeding or pain depends on the underlying cause. If gum disease is the culprit, dentists or periodontists may recommend improved oral hygiene at home, antibiotics, tooth scaling and root planing, osseous surgery, or laser periodontal surgery. For cases where gum disease isn't the cause, healthcare providers will conduct tests to determine if there are underlying health conditions such as diabetes, blood-clotting disorders, or vitamin deficiencies. Based on the diagnosis, appropriate treatment will be recommended.
Self-Care Measures at Home
If you experience gum bleeding or pain, there are several things you can do at home to try and alleviate the symptoms. Brushing your teeth two to three times a day, flossing once daily, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can all be helpful. Additionally, avoiding smoking is essential.
The Consequences of Ignoring Gum Bleeding or Pain
Ignoring gum bleeding or pain can have serious consequences. If gum disease is the cause and left untreated, it can erode the tissue, ligaments, and bone that support your teeth, leading to a cycle of infection, bad breath, and potentially tooth loss. If another health issue is causing the gum problems, the symptoms may worsen as the underlying condition progresses. It's therefore vital to seek a healthcare provider's advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Prevention of Gum Bleeding or Pain
In many cases, gum bleeding or pain can be prevented. Regular visits to the dentist and maintaining good oral hygiene at home can reduce the risk of gum disease. However, some causes, such as hormone changes, blood-clotting disorders, or leukemia, may be beyond our control.
When to Seek Professional Help
Gum bleeding or pain that doesn't stop within two weeks should prompt you to see a dentist or primary care physician. They will either recommend treatment for gum bleeding or address any underlying conditions.
Common Questions Answered
Some common questions related to gum bleeding or pain include what deficiencies can cause it (such as vitamin C or vitamin K deficiencies), when to be worried (if the bleeding occurs randomly or persists for more than two weeks), and how long it's safe to wait (while it's not usually an emergency, seeking help after two weeks is advisable to prevent underlying conditions from worsening).
Gum bleeding or pain is not something to be taken lightly. It can be a sign of various dental and overall health issues. By understanding the causes, seeking appropriate treatment, and practicing good oral hygiene and self-care, you can improve your oral health and prevent potential complications. Don't ignore these symptoms; consult a healthcare provider to ensure your gums and overall well-being are in the best shape possible.





 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile