The Impact of Aging on Your Oral Health: What You Need to Know
- Understanding How Aging Affects Oral Health
- Common Oral Health Issues in Older Adults
- How to Maintain Good Oral Health as You Age
- Dental Care Solutions for Aging Adults
- When to Consult a Dentist About Age-Related Oral Health Concerns
Understanding How Aging Affects Oral Health
Aging is a natural part of life, but it can have a significant impact on oral health. As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, and our mouths are no exception. Understanding how aging affects your oral health can help you take proactive steps to prevent or manage common issues.
Key Factors That Affect Oral Health with Age
Several factors contribute to oral health issues as people age:
- Dry Mouth: As we age, the production of saliva often decreases, leading to dry mouth. This condition can make it difficult to speak, swallow, and eat, and it increases the risk of cavities and gum disease.
- Gum Disease: Older adults are more susceptible to gum disease due to age-related changes in the immune system, as well as a lifetime of plaque buildup.
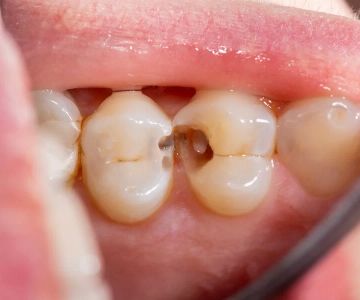
- Tooth Enamel Wear: Over time, tooth enamel can wear down, leading to tooth sensitivity and an increased risk of cavities.
Common Oral Health Issues in Older Adults
As people age, they are more likely to experience specific oral health issues. Understanding these issues can help you better manage your oral care routine and seek treatment when necessary.
Tooth Loss and Its Causes
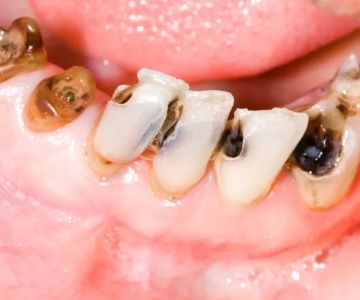
Tooth loss is a common issue for older adults. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Gum Disease: Untreated gum disease can lead to tooth loss if the gums and bone structures that support the teeth deteriorate.
- Cavities: Over time, untreated cavities can damage teeth to the point of loss.
- Accidents or Injury: Physical trauma to the mouth can also result in tooth loss.
Oral Cancer Risk
Older adults are at higher risk for developing oral cancer. Tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and prolonged exposure to the sun (especially for the lips) can all increase the risk of oral cancers. Regular dental checkups are crucial for early detection and successful treatment.
How to Maintain Good Oral Health as You Age
While aging can increase the risk of oral health problems, adopting a good oral care routine can help prevent or mitigate many of these issues. Here are some tips to maintain optimal oral health as you age:
Brush and Floss Regularly
Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles. This simple routine can prevent cavities, gum disease, and tooth loss.
Use a Mouthwash for Dry Mouth
If you suffer from dry mouth, use a mouthwash designed to help maintain moisture in the mouth. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can also help alleviate dryness.
Regular Dental Checkups
Regular visits to the dentist are essential for maintaining good oral health. Dentists can spot early signs of problems such as cavities, gum disease, or oral cancer, allowing for prompt treatment. Aim for a checkup at least twice a year, or more frequently if recommended by your dentist.
Dental Care Solutions for Aging Adults
If you're experiencing age-related oral health problems, there are several solutions available to help manage these issues and maintain a healthy smile.
Dental Implants
Dental implants are a popular solution for replacing missing teeth due to aging. These permanent solutions can restore both the function and appearance of your smile, allowing you to speak, eat, and smile with confidence.
Gum Disease Treatment
If gum disease is detected, treatment options such as scaling and root planing or gum surgery can help restore your gums to a healthy state. Your dentist may also recommend more frequent cleanings to manage the disease effectively.
When to Consult a Dentist About Age-Related Oral Health Concerns
If you're experiencing any of the following symptoms, it's time to consult a dentist:
- Persistent dry mouth that doesn't improve with over-the-counter remedies.
- Tooth sensitivity or pain when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods.
- Bleeding or swollen gums that don't heal.
- Noticeable changes in your teeth, such as shifting or loose teeth.
Early intervention can prevent further damage and ensure that your oral health remains in good condition throughout your life.


 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile