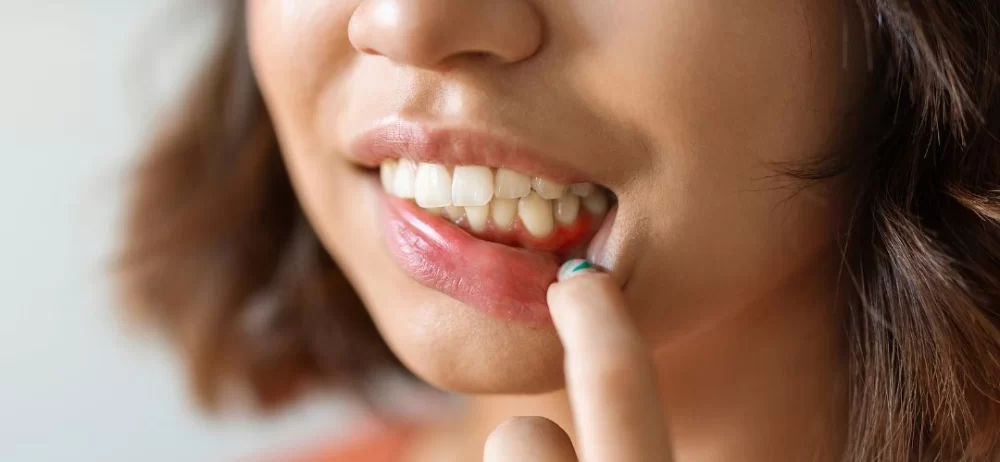

Understanding Receding Gums and Why Treatment Is Crucial
Receding gums is a common dental problem affecting millions of people in the United States. This condition occurs when the gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth or its root. As a result, the affected teeth can appear longer, and the gums become more vulnerable to infections, decay, and even tooth loss. Understanding the underlying causes and the best treatments for receding gums is essential in preventing further damage and maintaining oral health.
What Causes Receding Gums?
Several factors contribute to the development of receding gums. Some of the most common causes include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which contributes to gum disease and gum recession.
- Genetics: Some people are more prone to gum recession due to their genetic makeup, making it more difficult to prevent the condition.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and other hormonal shifts can increase the risk of gum recession, particularly in women.
- Age: As people age, the gums naturally begin to recede, making this condition more common among older adults.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco are significant contributors to gum disease and recession.
- Teeth Grinding: Bruxism, or grinding teeth, can exert excessive force on the gums and teeth, leading to gum recession over time.
How Receding Gums Affect Oral Health
Aside from aesthetic concerns, receding gums can have serious implications for overall oral health. Exposed tooth roots are more susceptible to decay, sensitivity, and infections. The gum recession may also increase the risk of tooth mobility and eventual tooth loss. Therefore, addressing this issue early on is crucial to preserving your teeth and maintaining a healthy smile.
Top Treatments for Receding Gums
If you're experiencing gum recession, the good news is that several treatments can help stop or even reverse the damage. Here’s a look at the best solutions for receding gums:
1. Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a non-surgical procedure often recommended for people with gum disease. This treatment involves cleaning the teeth thoroughly, removing plaque and tartar buildup from both above and below the gum line. Root planing smooths the root surfaces, which helps the gums reattach to the teeth, potentially reducing the severity of gum recession.
2. Gum Grafting
For more severe cases of receding gums, gum grafting may be required. This surgical procedure involves taking healthy gum tissue from another part of the mouth and attaching it to the areas where the gums have receded. There are several types of gum grafting, including connective tissue grafts, free gingival grafts, and pedicle grafts, all of which can help restore gum coverage and prevent further recession.
3. Pinhole Surgical Technique
The Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST) is a minimally invasive procedure for treating receding gums. During the procedure, a small hole is made in the gum tissue, and special instruments are used to gently reposition the gum tissue over the exposed tooth roots. This technique is less invasive than traditional gum grafting, requires no sutures, and has a quicker recovery time.
4. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is another advanced treatment option for receding gums. This procedure uses a laser to remove infected tissue and stimulate the regeneration of healthy gum tissue. Laser therapy is less invasive than traditional surgery, and patients typically experience less pain and a faster recovery.
5. Natural Remedies and Home Care
In addition to professional treatments, maintaining good oral hygiene at home is essential for preventing and managing receding gums. Some natural remedies that may help include:
- Saltwater Rinse: A gentle saltwater rinse can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria in the mouth.
- Aloe Vera: Applying aloe vera gel to the gums may soothe irritation and promote healing.
- Green Tea: Drinking green tea may help reduce gum inflammation due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
6. Preventing Gum Recession
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to gum health. Here are some tips to help you avoid receding gums:
- Brush Gently: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid brushing too hard, which can damage your gums.
- Floss Daily: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth, preventing gum disease.
- Avoid Tobacco: Smoking and using tobacco products can harm your gums and increase your risk of gum disease.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and exams to detect gum problems early.
Why It's Important to Seek Professional Help
While some mild cases of receding gums can be managed with home remedies and lifestyle changes, more severe cases often require professional intervention. Seeing a dentist or periodontist early in the process can help prevent further damage and save your teeth. Early treatment can also minimize the risk of complications such as tooth loss and gum infections.
Ignoring gum recession can lead to long-term oral health issues that may be costly and difficult to treat. If you notice any signs of gum recession, such as teeth appearing longer or increased tooth sensitivity, it’s important to consult with a dental professional as soon as possible.
Conclusion
Receding gums can be a serious dental problem, but with the right treatments, it’s possible to restore your gums and prevent further damage. From non-invasive laser therapy to advanced gum grafting techniques, there are several options available to help manage this condition. By maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking timely professional care, you can keep your gums healthy and your smile beautiful for years to come.






 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile