How to Treat Tooth Infection with Antibiotics: A Complete Guide
- 1. What is a Tooth Infection?
- 2. Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
- 3. Why Antibiotics are Used for Tooth Infection
- 4. Types of Antibiotics Used for Tooth Infection
- 5. How to Treat a Tooth Infection with Antibiotics
- 6. When to Seek Medical Attention
- 7. Conclusion
1. What is a Tooth Infection?
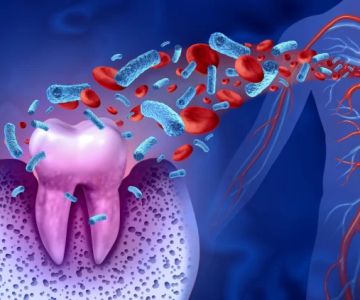
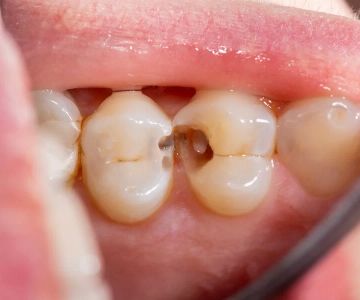
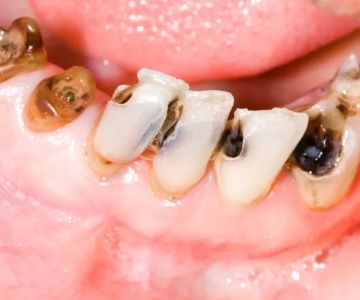
A tooth infection occurs when bacteria invade the tooth or the surrounding gums, causing pain, swelling, and, in some cases, fever. These infections often begin from untreated cavities or gum disease. It is important to address these issues promptly to avoid serious complications.
2. Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
The symptoms of a tooth infection can vary from mild to severe, but common signs include:
- Persistent tooth pain
- Swelling in the gums or face
- Fever
- Bad breath
- Tender or swollen lymph nodes
If you notice these symptoms, it's essential to seek treatment right away to avoid the infection spreading.
3. Why Antibiotics are Used for Tooth Infection
Antibiotics are often prescribed for tooth infections to control the spread of bacteria. These medications help to kill the bacteria causing the infection, reduce inflammation, and prevent the infection from spreading to other areas of the body, such as the jaw or bloodstream.
However, antibiotics are not a substitute for proper dental care, such as drainage of an abscess or a root canal procedure. They work best in conjunction with other treatments.
4. Types of Antibiotics Used for Tooth Infection
The most common antibiotics prescribed for tooth infections include:
- Amoxicillin: This is one of the most commonly used antibiotics for tooth infections, particularly if the infection is not severe.
- Clindamycin: Often used when a patient is allergic to penicillin, clindamycin helps fight infections by inhibiting bacterial growth.
- Metronidazole: This is sometimes prescribed for anaerobic bacterial infections, which are common in dental abscesses.
It is essential to take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider and complete the full course, even if you begin feeling better.
5. How to Treat a Tooth Infection with Antibiotics
Treating a tooth infection with antibiotics typically involves the following steps:
- Consultation: Visit your dentist or doctor for a diagnosis. They may perform X-rays to assess the extent of the infection.
- Prescription: If necessary, your doctor will prescribe an appropriate antibiotic based on the type of infection.
- Follow-up: After taking the antibiotics for a few days, your dentist may recommend additional treatments such as drainage or a root canal to fully address the infection.
- Prevention: Once the infection is controlled, follow proper oral hygiene to prevent further infections.
While antibiotics are effective, they should not be seen as a one-stop solution. Proper dental care and timely treatment are critical to avoiding recurring infections.
6. When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following signs, seek immediate medical attention:
- Severe swelling of the face or neck
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Fever that does not subside
- Increased pain despite taking antibiotics
Delaying medical care in these instances can lead to more severe health complications, so it’s important to act quickly.
7. Conclusion
Tooth infections can be painful and potentially dangerous, but with the proper care and antibiotics, they can be treated effectively. Remember that while antibiotics are essential in managing the infection, they work best when combined with proper dental procedures. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
If you're experiencing a tooth infection, don’t wait! Act now to prevent complications. For more information or to purchase the right antibiotics for your condition, click here to learn more about your treatment options.


 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile