Understanding Gum Disease and Its Treatment
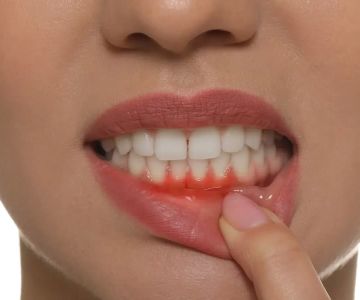
Gum disease, a common oral health issue, can progress from the early stage of gingivitis to more severe forms like periodontitis. It's crucial to understand the different stages and the appropriate treatments for each. Early detection and prompt intervention are key to successful recovery and prevention of further damage.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
There are various treatment approaches depending on the stage of gum disease. For minor cases of gingivitis, scaling can often do the trick by removing plaque and tartar. In more advanced cases, periodontal pocket reduction surgery or the use of antibiotics might be necessary. Maintaining good oral hygiene at home, such as regular brushing, flossing, and using the right toothbrush and flosser, is also essential for recovery and prevention.
Healing Time for Gingivitis
If you have the initial stage of gum disease, gingivitis, you can typically expect to heal and recover within 14 days of undergoing a deep cleaning, provided you take prescribed antibiotics and adhere to thorough oral hygiene practices like brushing and flossing. However, it's important to note that maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular dental check-ups are necessary to prevent the recurrence of gingivitis.
Challenges in Treating Advanced Gum Disease
Periodontitis and advanced periodontitis present more significant challenges. These stages cause irreversible damage to the gums and teeth. While the progression can be controlled with regular periodontal cleanings every 3 months and good oral hygiene, a complete cure is not achievable. This emphasizes the importance of seeking treatment at the earliest signs of gum disease.
Home Remedies and Tips for Oral Health
Home remedies like saltwater rinses can be beneficial for healing gum tissues. Choosing the right toothbrush, brushing techniques, and flossing regularly are vital for maintaining oral health. Additionally, using a water flosser can be more effective in reaching hard-to-access areas and preventing the buildup of plaque and tartar.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the time it takes to treat gum disease varies depending on the stage and the individual's response to treatment. Early intervention and consistent oral hygiene practices are paramount. Gingivitis can often be reversed within a couple of weeks with proper care, but advanced gum disease requires lifelong management. Remember, your oral health is an investment in your overall well-being, so take it seriously and seek professional dental advice when needed.






 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile