- 1-Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact on Oral Health
- 2-How Diabetes Affects Gums and Leads to Oral Problems
- 3-Symptoms of Diabetes-Related Oral Health Issues
- 4-How to Prevent Tooth and Gum Problems in People with Diabetes
- 5-Real-Life Stories of Managing Oral Health with Diabetes
1. Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact on Oral Health
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). When blood sugar levels are poorly controlled, it can lead to various complications, including oral health problems. People with diabetes are more likely to develop gum disease, dry mouth, and tooth decay. This is because high blood sugar can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections in the mouth, which increases the risk of dental issues.
Additionally, diabetes can reduce the blood flow to the gums, impairing the ability to heal, and increasing the likelihood of infections. With proper management, however, people with diabetes can minimize the impact of these oral health problems.
2. How Diabetes Affects Gums and Leads to Oral Problems
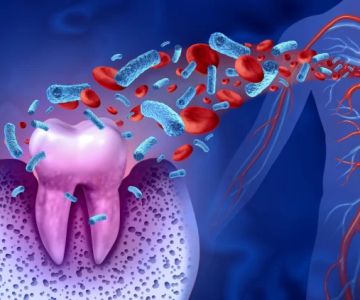
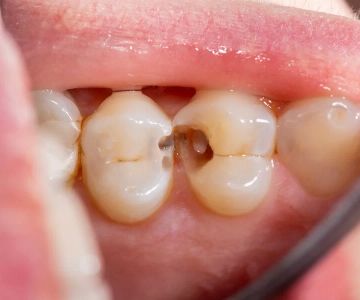
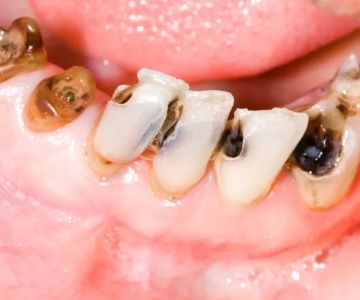
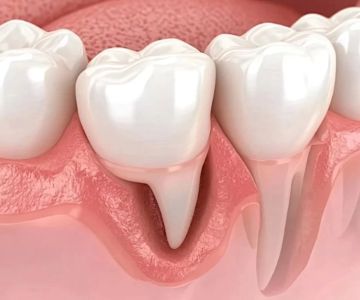
One of the most common oral health issues associated with diabetes is gum disease (also known as periodontal disease). This is because high blood sugar levels can promote the growth of bacteria in the mouth, which leads to plaque buildup on teeth. Plaque can cause gums to become inflamed, red, and bleed easily. If left untreated, this condition can progress to gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease, and potentially to more severe forms like periodontitis, which can cause tooth loss.
In addition to gum disease, people with diabetes are also more prone to developing dry mouth (xerostomia). High blood sugar levels can decrease the production of saliva, leaving the mouth dry and increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum infections.
4. How to Prevent Tooth and Gum Problems in People with Diabetes
People with diabetes can take steps to prevent tooth and gum problems by managing their blood sugar levels and practicing good oral hygiene. Here are some tips to help maintain healthy teeth and gums:
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping your blood sugar within the target range is the most important factor in preventing diabetes-related oral health problems. Consistently high blood sugar levels increase the risk of infections, including gum disease.
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles. This is essential for preventing gum disease and cavities.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Regular dental checkups are vital for catching early signs of gum disease and tooth decay. Make sure your dentist is aware of your diabetes so they can monitor your oral health closely.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to combat dry mouth and help maintain healthy saliva flow. This also helps rinse away food particles and bacteria.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of gum disease in people with diabetes. Quitting smoking can help protect your gums and improve overall oral health.
By following these tips and managing your diabetes, you can greatly reduce the risk of developing tooth and gum problems.
5. Real-Life Stories of Managing Oral Health with Diabetes
Many people with diabetes have successfully managed their oral health with the right care and attention. For example, Lisa, a 40-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes, struggled with gum disease and dry mouth for years. After working closely with her dentist and doctor to control her blood sugar levels and following a strict oral care routine, her gums improved significantly, and her dry mouth symptoms were alleviated. Lisa was able to keep her teeth healthy and prevent further dental issues.
Another example is John, a 55-year-old man with type 1 diabetes, who experienced frequent tooth decay due to dry mouth. By drinking more water throughout the day and using fluoride mouthwash, along with regular dental visits, he was able to reverse the effects of dry mouth and protect his teeth from further decay.
These real-life stories show how proper diabetes management, combined with good oral hygiene, can help protect teeth and gums from the adverse effects of diabetes.


 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile