What is Gum Recession?
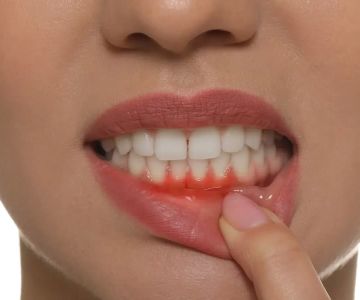
Gum recession occurs when gum tissue pulls away from teeth, exposing the roots. This can be caused by various factors such as aggressive brushing, smoking, periodontal disease, and genetics. Gum recession can make teeth more vulnerable to cavities and sensitivity. It can range from mild to severe and may affect one or multiple teeth. People of all ages can experience gum recession, but it's more common in those over 65. Poor oral hygiene often contributes, but sometimes it's simply due to a genetic predisposition to thin gum tissue.
Symptoms and Causes of Gum Recession
The most obvious symptom of gum recession is the exposure of tooth roots. Other warning signs include pain or discomfort near the gum line, sensitivity to heat, cold, and sweets, as well as sensitivity during brushing, flossing, and dental cleanings. Left untreated, it can lead to serious problems like bone loss, tooth mobility, or even tooth loss. The causes of gum recession include brushing too hard, plaque and tartar buildup, periodontal disease, trauma, abnormal tooth positioning, smoking, and lip or tongue piercings.
Diagnosis and Tests for Gum Recession
Your dentist can diagnose gum recession during a routine examination by measuring the amount of gum recession on each tooth using a special instrument called a periodontal probe. They will also measure the periodontal pockets around each tooth to assess the extent of the problem. Healthy pockets measure between 1 and 3 millimeters, while those with gingivitis measure 4 millimeters. If you have periodontal disease, the pockets will measure 5 millimeters or higher.
Management and Treatment of Gum Recession
Unfortunately, receding gums cannot grow back. However, you can take measures to prevent the condition from worsening and reduce sensitivity. Your dentist can apply fluoride varnish or other desensitizing agents, and you can use desensitizing toothpaste at home. The best toothpaste for gum recession contains ingredients like potassium nitrate, stannous fluoride, arginine, and strontium chloride. The treatment for gum recession depends on the cause. Mild cases may be improved with nonsurgical treatments like topical antibiotics, dental bonding, or orthodontics. In more severe cases, gum recession surgery, such as gum grafting, is often necessary. During gum graft surgery, a gum graft is used to replace the missing gum tissue, and the recovery time varies depending on several factors.
Prevention of Gum Recession
Although gum recession can't always be prevented, especially if you have a genetic predisposition, you can significantly reduce the risk by maintaining proper teeth and gum care. This includes brushing thoroughly twice a day, flossing once a day, using an antimicrobial mouthwash twice a day, following your dentist's recommendation for teeth cleanings, using a soft-bristled toothbrush, and avoiding smoking and chewing tobacco. Seeing your dentist at the first sign of gum recession is crucial.
Outlook and Prognosis of Gum Recession
If you have mild gum recession, nonsurgical treatments may be attempted. For moderate to severe gum recession, you may be referred to a periodontist or oral surgeon for a gum grafting consultation. Gum recession cannot be cured, but it can be managed with proper treatment and care.
Living With Gum Recession
If you notice signs of gum recession such as increased visibility of tooth roots or increased tooth sensitivity, it's important to contact your dentist or periodontist promptly. It's also beneficial to ask your healthcare provider questions about the severity of your gum recession, available nonsurgical options, recommended gum grafting surgery, the chances of recurrence, and the frequency of teeth cleanings. Untreated gum recession can have a significant impact on your oral health, so early detection and treatment are essential for maintaining optimal oral health.
Gum recession is a significant oral health concern that can have various causes and symptoms. While it cannot be reversed once it occurs, proper dental treatment and preventive measures can help manage the condition and prevent further deterioration. Regular dental check-ups, maintaining good oral hygiene, and seeking prompt treatment at the first sign of problems are key to preserving your oral health and preventing the negative consequences of gum recession.





 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile