Who Checks for Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer, which includes cancers of the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, roof, and floor of the mouth, is a serious and often overlooked condition. Regular check-ups for oral cancer are crucial for early detection, and catching it early can make a significant difference in treatment success. But who exactly checks for oral cancer, and how do they do it?
Typically, the responsibility for checking for oral cancer falls to dental professionals. Dentists are trained to recognize the signs and symptoms of oral cancer during routine dental exams. However, other healthcare providers, including doctors and oral surgeons, may also play a role in the diagnosis and management of oral cancer. It’s important for everyone, especially those who are at higher risk, to have regular screenings and to understand the process of oral cancer detection.
How Dentists Check for Oral Cancer
When you visit the dentist, they don’t just clean your teeth or fill cavities. One of the critical aspects of a dental check-up is the oral cancer screening. Dentists are trained to look for abnormal growths, sores, or lesions that may indicate oral cancer.
1. Visual Examination
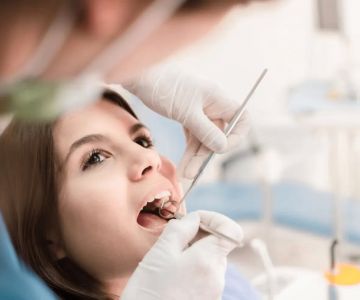
The first step in the screening process is a thorough visual examination of your mouth. The dentist will look for any signs of irregularities, such as sores, red or white patches, and swelling. They will also examine the roof and floor of the mouth, gums, cheeks, tongue, and the inside of the lips for any unusual growths or changes in appearance. During this examination, the dentist may also use a special light to detect abnormal tissues.
2. Physical Examination
Next, the dentist will feel the tissues of the mouth and neck to check for any lumps or abnormalities. This part of the exam helps the dentist detect any swollen lymph nodes or hard masses that may suggest cancerous growths. The dentist will gently palpate the neck, jaw, and lymph nodes to look for any signs of oral cancer that could be spreading to other areas.
3. Biopsy Referral
If the dentist detects any suspicious areas or growths, they may refer you to an oral surgeon or another specialist for a biopsy. A biopsy is the definitive test to determine if a lesion is cancerous. The biopsy involves removing a small tissue sample from the affected area to be examined under a microscope in a lab.
Who Else Checks for Oral Cancer?
While dentists are the primary healthcare providers who check for oral cancer, other specialists are also involved in the diagnosis and treatment of the condition. It’s important to be aware of the roles these professionals play and when you might need to see them.
1. Primary Care Doctors
Your primary care doctor may also check for oral cancer during routine health check-ups, especially if you have risk factors such as tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, or a family history of cancer. They will typically perform a visual exam of the mouth and may refer you to a dentist or specialist if they notice anything concerning.
2. Oral Surgeons
If a biopsy is needed or if surgery is required to remove cancerous tissue, an oral surgeon is the specialist who performs the procedure. Oral surgeons are trained in both the diagnosis and surgical treatment of oral diseases, including oral cancer. They play a crucial role in both early detection and treatment.
3. Head and Neck Surgeons
In some cases, head and neck surgeons, or otolaryngologists, may become involved in the care of a patient with oral cancer. These specialists are experts in the medical and surgical management of cancers in the head and neck area. If cancer is detected in the mouth or throat, they may help in further treatment, including surgery or radiation therapy.
Risk Factors for Oral Cancer
Understanding the risk factors for oral cancer is essential for identifying those who are most likely to benefit from regular screenings. While oral cancer can affect anyone, certain lifestyle choices and habits increase the risk of developing the condition. Some of the most common risk factors include:
1. Tobacco Use
Smoking and chewing tobacco are the leading causes of oral cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco products can damage the cells in the mouth, leading to the development of cancerous lesions. Even smokeless tobacco, like chewing tobacco, significantly increases the risk of oral cancer.
2. Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol use is another significant risk factor. The combination of tobacco and alcohol use increases the risk of developing oral cancer significantly. Studies show that people who both smoke and drink have a much higher risk of oral cancer compared to those who only engage in one of these behaviors.
3. HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
Recent studies have also linked the human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly strains of the virus that affect the throat and mouth, to oral cancer. HPV-related oral cancers are more common in younger individuals and may not always have the traditional risk factors, such as smoking or drinking.
4. Poor Nutrition
A diet low in fruits and vegetables can also increase the risk of oral cancer. The antioxidants and vitamins found in fruits and vegetables help protect the body from harmful substances that could lead to cancer development.
5. Family History
If there’s a family history of oral cancer, your risk of developing the disease may be higher. Genetics can play a role in the development of many types of cancer, including those of the mouth and throat.
Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection is one of the most crucial elements in the successful treatment of oral cancer. That’s why regular oral cancer screenings are essential for everyone, particularly those at higher risk. While the dentist plays the primary role in detecting oral cancer, it’s also important for patients to be aware of changes in their mouth and seek prompt medical attention if they notice any signs of trouble.
1. Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Some common symptoms of oral cancer that should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider include:
- Persistent mouth sores that do not heal within two weeks
- Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or chewing
- Unexplained pain in the mouth or jaw
- Lumps or thickened areas inside the mouth or on the neck
- Persistent hoarseness or a sore throat
2. Preventative Measures
While not all cases of oral cancer can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Avoid tobacco products, including smoking and chewing tobacco
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Get vaccinated for HPV, which can help reduce the risk of HPV-related oral cancers
- Use sunscreen to protect your lips from the sun
Why Choose Dentistry Toothtruth for Oral Cancer Screening
At Dentistry Toothtruth, we are committed to providing the highest quality care for our patients. Our professional team offers comprehensive oral cancer screenings as part of regular dental check-ups. We use the latest technology and techniques to detect potential issues early, ensuring that you receive the best possible treatment if needed.
If you're due for an oral cancer screening or want to learn more about how to protect your oral health, visit us today. At Dentistry Toothtruth, your health and well-being are our top priority, and we're here to help you keep your smile bright and healthy!




 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile