How Gum Disease Can Worsen Chronic Conditions Like Arthritis
- Impact of Gum Disease on Arthritis
- The Link Between Gum Disease and Chronic Conditions
- How to Manage Gum Disease to Improve Arthritis Symptoms
- Case Studies and Examples
- Get Help from Experts
1. Impact of Gum Disease on Arthritis
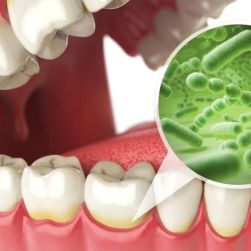
Gum disease, particularly periodontal disease, can have far-reaching effects on overall health, including worsening chronic conditions like arthritis. Studies have shown that the inflammation caused by gum disease can amplify the inflammatory processes in the joints, leading to more severe arthritis symptoms. The bacteria from the infected gums can enter the bloodstream, triggering systemic inflammation that affects joints and connective tissues.
This means that individuals with arthritis who also suffer from gum disease may experience increased pain, stiffness, and swelling. It’s essential to address gum disease early to prevent it from exacerbating arthritis or any other chronic condition.
2. The Link Between Gum Disease and Chronic Conditions
The connection between oral health and chronic diseases is becoming increasingly recognized by healthcare professionals. Inflammation in the mouth can spill over into other parts of the body, affecting organs and systems beyond just the teeth and gums. When gum disease is left untreated, it can not only lead to tooth loss but also contribute to the progression of other health issues, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis.
For individuals with arthritis, managing gum health becomes even more critical. Oral health and arthritis share a common risk factor: inflammation. Inflammation in the gums can worsen the joint inflammation seen in arthritis patients, making pain and mobility issues more challenging to control.
3. How to Manage Gum Disease to Improve Arthritis Symptoms
Effective management of gum disease involves regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and good daily oral hygiene practices. Brushing and flossing regularly can help prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria that cause gum disease. Additionally, using an antibacterial mouthwash can reduce the spread of harmful bacteria.
If you have arthritis, it’s important to consult with both your dentist and rheumatologist to create a plan that addresses both conditions simultaneously. Managing your oral health may not only prevent the worsening of gum disease but also help alleviate arthritis symptoms over time. In some cases, treating gum disease has been shown to improve joint health and reduce pain in arthritis patients.
4. Case Studies and Examples
Let’s look at a few real-world examples to understand how managing gum disease has helped those with arthritis:
Case 1: Sarah, a 56-year-old woman diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, noticed that her joint pain worsened significantly when her gum disease was left untreated. After receiving professional treatment for her gums and improving her oral hygiene, Sarah reported a noticeable decrease in her joint inflammation, and her arthritis symptoms became more manageable.
Case 2: James, a 60-year-old man with osteoarthritis, began using an antibacterial mouthwash as part of his oral health routine. Over several months, his symptoms of joint pain improved, and his dentist confirmed that the bacteria from his gums had been contributing to the increased inflammation in his joints.
5. Get Help from Experts
If you are struggling with both gum disease and arthritis, it’s essential to seek professional help. Both conditions require targeted care, and a multidisciplinary approach can offer the best results. Consult your dentist for advice on managing gum health, and talk to your rheumatologist about integrating gum disease treatment into your arthritis management plan.
For more information on how gum disease can affect chronic conditions and for expert advice, visit Dentistry Toothtruth.