How Do Doctors Check for Oral STDs?
Oral sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are a concern for many, yet they often go undiagnosed due to a lack of visible symptoms. Just as with any other STDs, oral infections can be serious and require professional diagnosis and treatment. So, how do doctors check for oral STDs? In this article, we’ll explore the diagnostic methods, common oral STDs, and what you can expect during a doctor’s visit for an oral STD check-up.
1. Common Oral STDs and Their Symptoms
Before delving into how doctors check for oral STDs, it’s essential to understand the types of infections that can affect the mouth. Some common oral STDs include:
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) – Causing cold sores around the mouth and lips, HSV is one of the most common oral STDs. Symptoms include painful blisters and itching.
- Gonorrhea – While more commonly associated with genital infections, gonorrhea can also affect the throat, causing symptoms like a sore throat, redness, and difficulty swallowing.
- Syphilis – Early stages of syphilis can cause painless sores in the mouth or lips, known as chancres, which may go unnoticed.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) – Certain strains of HPV can cause warts in the mouth and throat, leading to potential discomfort or changes in speech or swallowing.
These infections can manifest in various ways, including visible sores, blisters, discomfort while eating or swallowing, and more. However, many oral STDs can also be asymptomatic, which is why regular check-ups are essential for diagnosis.
2. Initial Consultation and Physical Examination
When you visit a healthcare provider for a potential oral STD, the first step typically involves a thorough consultation. Your doctor will ask about your sexual history, symptoms, and any concerns you may have. It’s important to be open and honest with your provider, as this information will help guide the diagnostic process.
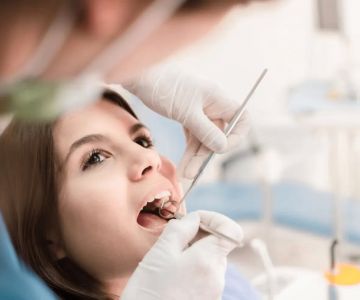
During the physical examination, your doctor will visually inspect your mouth, throat, and lips for any signs of infection, such as:
- Visible sores, blisters, or ulcers
- Redness or inflammation in the mouth or throat
- Enlarged lymph nodes
In addition to visual inspection, your doctor may also perform a gentle palpation to feel for any unusual bumps or masses that could indicate the presence of an infection.
3. Laboratory Tests and Swabs
If your doctor suspects that you have an oral STD based on your symptoms and physical examination, they may recommend laboratory testing to confirm the diagnosis. The most common method for testing oral STDs is through the collection of a sample from the affected area. This can involve:
- Swabbing the sores or blisters – For HSV or syphilis, a swab can be taken from the affected area to test for the presence of the virus or bacteria.
- Throat swabs – For gonorrhea or chlamydia infections, your doctor may take a swab of your throat to check for bacteria.
- Blood tests – For certain infections, such as syphilis or HIV, your doctor may order a blood test to check for antibodies or viral markers.
The collected samples will be sent to a laboratory, where they will be tested for the specific pathogen causing the infection. Results can take anywhere from a few days to a week, depending on the type of test.
4. How Accurate Are Oral STD Tests?
Oral STD tests are generally accurate, but the effectiveness depends on several factors, including the type of infection and the stage of the disease. For example, herpes tests are most accurate when sores are actively present, while gonorrhea testing is more reliable when symptoms like a sore throat are present. It’s important to note that some STDs, like syphilis, can be challenging to detect without the right tests.
If your test results come back negative but you continue to experience symptoms, it’s essential to follow up with your doctor. A repeat test may be necessary, especially if you’re at high risk for oral STDs.
5. Treatment Options for Oral STDs
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, your doctor will discuss treatment options based on the specific infection. Treatment for oral STDs varies widely depending on the pathogen involved:
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) – Antiviral medications such as acyclovir or valacyclovir can help manage outbreaks and reduce symptoms.
- Gonorrhea – Gonorrhea is treated with antibiotics, usually a combination of ceftriaxone and azithromycin, to clear the infection.
- Syphilis – Early-stage syphilis is treated with a single dose of penicillin, while later stages may require more extensive treatment.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) – HPV-related oral warts can be treated with topical medications or surgical removal in some cases.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully when taking medication, and always complete the full course of treatment to prevent recurrence or resistance.
6. Preventing Oral STDs
The best way to prevent oral STDs is to practice safe sexual behaviors, including:
- Using barrier methods, such as condoms or dental dams, during oral sex
- Getting vaccinated against preventable infections, such as HPV
- Engaging in open and honest communication with partners about sexual health
Regular check-ups and early detection can also help prevent the spread of oral STDs. If you have concerns about your sexual health, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider for advice and testing.




 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile