Understanding Gum Tissue Damage
Gum tissue damage, often associated with periodontal disease, is a serious issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Periodontal disease is an inflammation and infection of the gums and the bone that supports the teeth. Poor oral hygiene is a common cause, but genetics and certain health conditions can also increase the risk.
Symptoms and Stages of Gum Tissue Damage
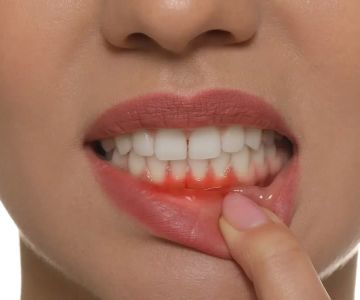
The symptoms of gum tissue damage can vary. Early signs may include reddish or purplish gums, bleeding, soreness, and bad breath. As the condition progresses, loose teeth, gum recession, and pain when chewing may occur. There are four stages of gum tissue damage: gingivitis, mild periodontitis, moderate periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis. Each stage brings increasing severity and potential complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Dental plaque buildup is the primary cause of gum tissue damage. Poor oral hygiene allows plaque to accumulate, leading to infection. Risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, hormonal changes, stress, genetics, and heart disease can also contribute to the development of gum tissue damage. Additionally, the bacteria that cause gum disease can be passed from person to person through prolonged contact.
Diagnosis and Tests
Dentists diagnose gum tissue damage during routine examinations by looking for plaque buildup, assessing symptoms, and measuring the pockets around the teeth. Periodontists may use additional tests such as X-rays to evaluate the extent of bone loss. A comprehensive assessment helps determine the severity of the condition and the appropriate treatment plan.
Management and Treatment Options
While gum tissue damage is not curable, it is manageable. Early detection and treatment are crucial. For mild cases, improved oral hygiene and routine dental cleanings may be sufficient. More advanced cases may require scaling and root planing, pocket reduction surgery, bone grafts, gum grafts, or guided tissue regeneration. Newer techniques like LANAP and platelet-rich fibrin/plasma therapy offer alternative approaches.
Prevention and Outlook
Preventing gum tissue damage is possible through consistent and proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing, flossing, and using antibacterial mouthwash. Avoiding smoking and maintaining regular dental visits also play essential roles. The outlook for individuals with gum tissue damage depends on the severity and the effectiveness of treatment. Early intervention can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of further complications.
In conclusion, gum tissue damage is a significant oral health concern that requires attention and proactive measures. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is essential for maintaining healthy gums and teeth. By adopting good oral hygiene habits and seeking timely dental care, individuals can minimize the risk of gum tissue damage and its potential negative impact on overall health.





 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile