The Connection Between Heart Disease and Gum Disease: How Oral Health Impacts Cardiovascular Health
- 1. What Is Gum Disease?
- 2. How Gum Disease Affects Heart Health
- 3. Scientific Research Linking Gum Disease to Heart Disease
- 4. Preventing Gum Disease and Protecting Your Heart
1. What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a common yet often overlooked condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It starts with the accumulation of plaque—a sticky, bacteria-filled film that forms on your teeth—and, if left untreated, can progress from gingivitis (the mildest form) to more severe periodontitis. The symptoms can range from bleeding gums to tooth loss, but it often remains unnoticed until it becomes more serious.
2. How Gum Disease Affects Heart Health
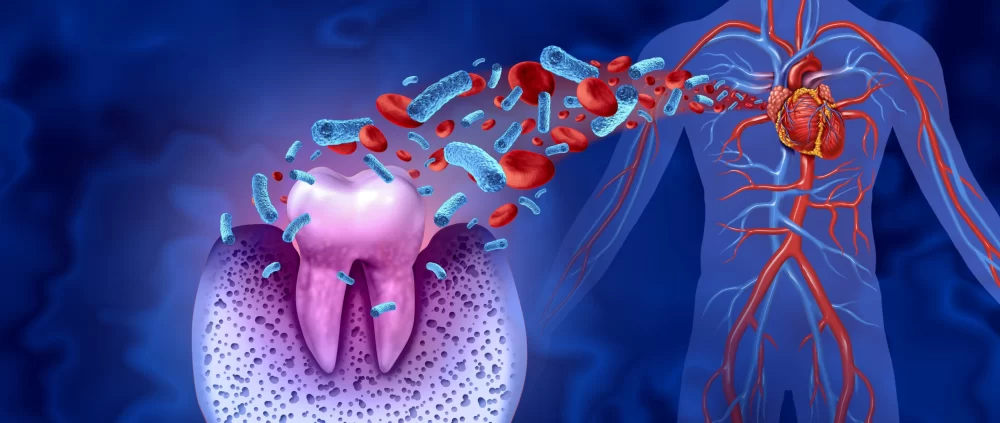
At first glance, it might seem like your gums and your heart don't have much in common. However, research has shown a significant link between gum disease and cardiovascular health. Here's how poor oral hygiene can increase your risk of heart disease:
2.1. Inflammation and Bacteria
Gum disease triggers chronic inflammation in the body. When bacteria from infected gums enter the bloodstream, they can contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This narrowing of the arteries can significantly increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
2.2. Increased Risk of Blood Clots
The bacteria from gum disease can also lead to an increased tendency for blood clots. These clots can disrupt the normal flow of blood to the heart, raising the risk of heart attacks or other cardiovascular complications.
2.3. Shared Risk Factors
Both gum disease and heart disease share common risk factors, such as smoking, diabetes, and poor diet. People who smoke or have diabetes are more likely to develop gum disease, which, in turn, exacerbates the risk of heart problems. Managing these shared risk factors is key to protecting both your gums and your heart.
3. Scientific Research Linking Gum Disease to Heart Disease
Numerous studies have examined the connection between gum disease and heart disease, and while the exact mechanism is still under investigation, the association is undeniable. For instance, a study published by the American Heart Association found that people with severe periodontal disease are almost twice as likely to suffer from heart disease compared to those without gum disease. Furthermore, research suggests that improving oral health through regular dental checkups can reduce the risk of heart disease.
One well-known example is a study conducted in 2019 that followed over 1,500 people for a period of 10 years. The results indicated that those with poor gum health had a significantly higher risk of developing cardiovascular conditions, including heart attacks and strokes. This research underscores the importance of oral health as part of a comprehensive approach to cardiovascular care.
4. Preventing Gum Disease and Protecting Your Heart
Fortunately, both gum disease and heart disease can be prevented with the right lifestyle choices. Here are some actionable steps you can take to reduce the risk of both:
4.1. Practice Good Oral Hygiene
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing regularly, and visiting your dentist for routine cleanings are essential for preventing gum disease. Keeping your gums healthy can directly reduce the inflammation that may impact your heart.
4.2. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a major contributor to both gum disease and heart disease. Quitting smoking can drastically reduce your risk for both conditions, helping your gums heal and improving cardiovascular health.
4.3. Control Your Blood Sugar
If you have diabetes, managing your blood sugar levels is crucial. High blood sugar weakens the immune system and makes it harder for the body to fight infections, including those in the gums. Keeping diabetes under control can lower your risk for gum disease and help protect your heart.
4.4. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains not only benefits your gums but also supports your cardiovascular health. Foods like leafy greens, nuts, and fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that help prevent both gum disease and heart disease.
4.5. Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups allow your dentist to catch any signs of gum disease early, before it can cause significant damage. Early treatment can help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of developing heart-related issues.







 Westgate Dental Arts
Westgate Dental Arts Coventry Family Dental
Coventry Family Dental Familia Dental
Familia Dental Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS
Dr. Daniel S. Fife, DDS Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD
Dentistry At Suburban Square: Michael I. Wollock, DMD Comfort Care Dental
Comfort Care Dental The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy
The Importance of Oral Health Education During Pregnancy for a Healthy Pregnancy Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems
Why Skipping Dental Checkups Can Lead to Bigger Oral Health Problems Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health
Best Tips for Brushing Your Teeth Properly for Healthy Gums: Essential Techniques for Oral Health Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations
Advantages of Porcelain Dental Restorations How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues
How Can Diabetes Cause Tooth and Gum Problems? Preventing and Managing Oral Health Issues Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile
Healthy Habits for Promoting Good Oral Health and Hygiene: Tips for a Healthy Smile